前言
经过上一节我们初步定义了一些标签的规范: prometheus + grafana 实战篇(1) - 定义标签组和规范, 本节我们来讲一下怎么监控 nginx
nginx
nginx 作为最受欢迎的 web server 之一,我的不少文章都有涉及到 nginx, 这边不再赘述。
我们假设在使用 prometheus 采集 nginx 之前,我们线上环境已经有 nginx 服务来跑了。
关于 nginx 的安装,可以看我的这一篇文章: CentOS 7 安装 Nginx
1 | [root@VM-16-223-centos sbin]# netstat -anlp | grep 80 |
nginx-vts-export
prometheus 常用的 nginx 的导出器,目前比较常用的是 nginx-vts-exporter
nginx_vts_exporter 依赖 nginx 的这个 nginx-module-vts 模块, 因此我们要先在 nginx 上重新编译安装 nginx-module-vts 模块
1. nginx 重新编译安装 nginx-module-vts 模块
直接从 github 下载 zip 包: 下载地址
1 | # 解压下载的 .tar.gz 的包 |
上面要注意一个细节,就是 configure 配置的时候,原先装的 nginx 是什么配置,就直接在原先的配置补上这两个配置即可:1
--with-http_stub_status_module --add-module=nginx-module-vts
比如我是白板配置,那么 configure arguments 就是: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx1
2
3
4[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-1.18.0]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.18.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx
如果之前就有支持 ssl 模块,那么就应该是:1
--prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_ssl_module
因此不管原先的 configure arguments 是什么,直接在后面补上我们新增的这两个配置即可
刚才已经编译完了,接下来不要进行安装执行 make install, 否则就是覆盖安装,原来的 nginx 还有一堆的配置文件,不能被覆盖。我们应该只覆盖编译出来的 nginx 可执行程序
也就是:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9# 先停止服务
[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-1.18.0]# sudo systemctl stop nginx.service
# 旧的可执行程序拷贝出来
[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-1.18.0]# cp /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx.bak
# 用新的替换旧的可执行程序
[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-1.18.0]# cp ./objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
cp: overwrite ‘/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx’? y
# 最后启动服务
[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-1.18.0]# sudo systemctl start nginx.service
接下来查看模块是否有成功编译进去:1
2
3
4[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-1.18.0]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.18.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --add-module=nginx-module-vts
接下来修改配置文件 nginx.conf, 将这个统计启动,在 http 里面 和 server 里面,各补上这个:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-1.18.0]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
#---隐藏其他配置
http {
#---隐藏其他配置
vhost_traffic_status_zone;
vhost_traffic_status_filter_by_host on;
server {
#---隐藏其他的路由
location /status {
vhost_traffic_status_display;
vhost_traffic_status_display_format html;
}
}
}
其实就是开启流量统计,有开放一个路由(/status)用来显示详情,接下来重启 nginx,然后直接访问这个 status 路由,就可以看到了
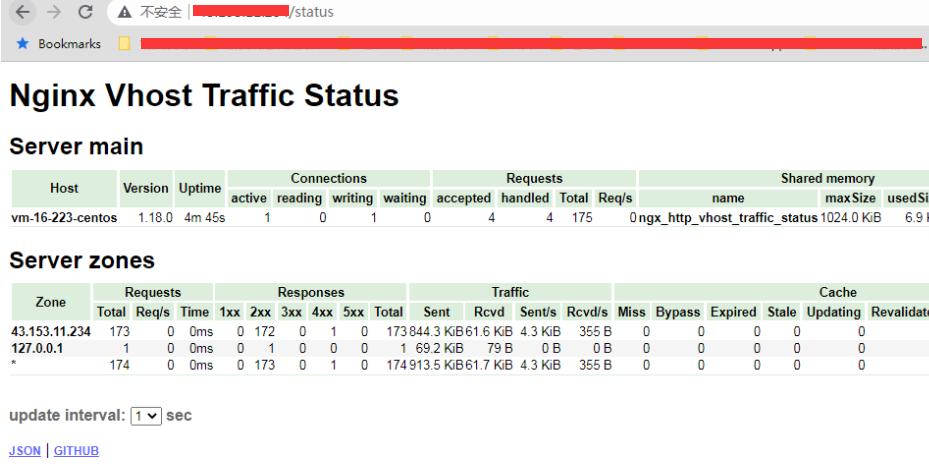
这边说一下 http 下面配置的这两个参数:1
2vhost_traffic_status_zone;
vhost_traffic_status_filter_by_host on;
这两个配置就是用来收集流量状态信息的,其中:1
vhost_traffic_status_filter_by_host on;
开启此功能,在 nginx 配置有多个 server_name 的情况下,会根据不同的 server_name 进行流量的统计,否则默认会把流量全部计算到第一个 server_name 上
当然如果有不想统计流量的 server 区域, 那么就可以禁用 vhost_traffic_status,比如:1
2
3server {
... vhost_traffic_status off; ...
}
这样子这一台虚拟主机就不会统计
2. 安装 nginx-vts-export 导出器
既然 nginx 的模块配置好了, 那么接下来就是安装这个 vts 的 exporter 了
一样下载 .tar.gz 包 (要下载 0.10.3 版本才有二进制包): 下载地址
具体:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32# 解压
[root@VM-16-223-centos local]# tar -zxvf nginx-vts-exporter-0.10.3.linux-amd64.tar.gz
nginx-vts-exporter-0.10.3.linux-amd64/
...
# 重命名
[root@VM-16-223-centos local]# mv nginx-vts-exporter-0.10.3.linux-amd64 nginx-vts-exporter
# 设置自启动
[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-vts-exporter]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx-vts-exporter.service
[Unit]
Description=nginx_vts_exporter
Documentation=https://github.com/hnlq715/nginx-vts-exporter
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx-vts-exporter/nginx-vts-exporter -nginx.scrape_uri http://localhost/status/format/json
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-vts-exporter]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-vts-exporter]# systemctl enable nginx-vts-exporter
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx-vts-exporter.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx-vts-exporter.service.
[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-vts-exporter]# systemctl start nginx-vts-exporter
[root@VM-16-223-centos nginx-vts-exporter]# systemctl status nginx-vts-exporter
● nginx-vts-exporter.service - nginx_vts_exporter
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx-vts-exporter.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2022-12-28 17:02:03 CST; 8s ago
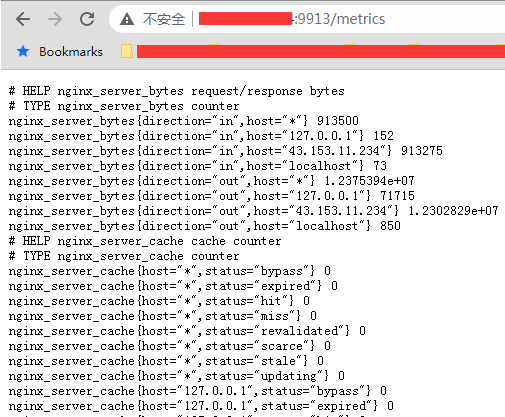
接下来请求 mertics 接口试试:
3. 接入 prometheus 并接入 grafana 模板
接下来就是接入 prometheus 抓取了, 因为我这边按照服务类型分别用文件服务发现的方式,因此这一台主机就加到 file_sd/server-nginx.yml 这个文件1
2
3
4- job_name: "server-nginx"
file_sd_configs:
- files:
- file_sd/server-nginx.yml
1 | - targets: |
这样子就可以抓取了,然后接下来再接入到 grafana 的模板中,可以用这个模板: 2949-nginx-vts-stats
所以最后的结果就是:
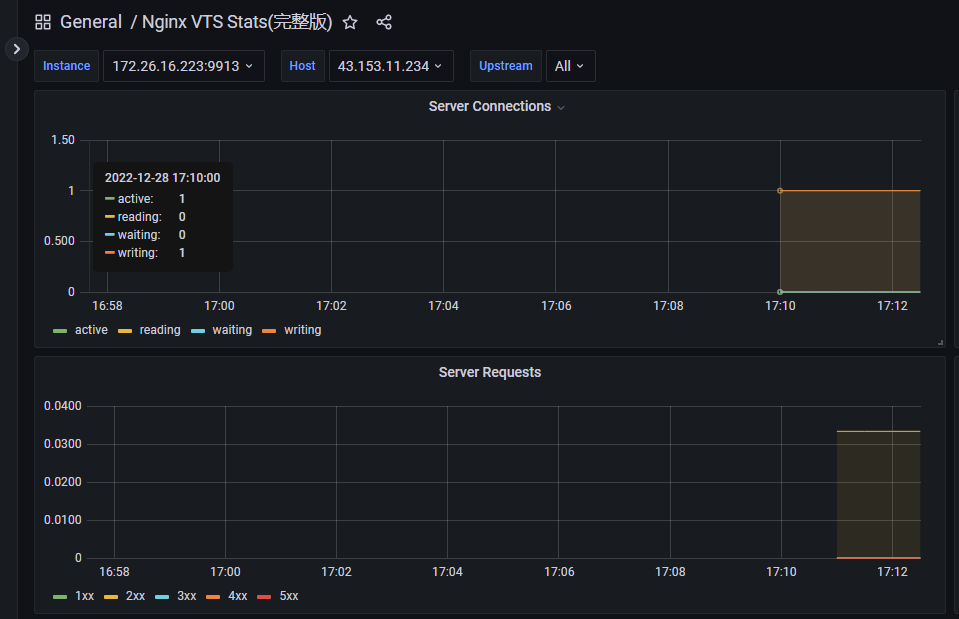
但是后面看了一下,他统计的数据,有状态码,有各个站点 host 的流量以及响应时间:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8# Filter Requests
nginx_upstream_requests{code="1xx", filter="country", filterName="BY"} 0
# Filter Bytes
nginx_upstream_bytes{direction="in", filter="country", filterName="BY"} 0
# Filter Response time
nginx_upstream_responseMsec{filter="country", filterName="BY"} 99
但是我发现我最关注的两个维度没有:
- 每一个路由 api 的请求数,以及请求方法,状态码
- 每一个路由 api 的响应时间
因此我查了一下官方文档,该导出器其实并没有去采集每一个站点的每一个请求的数据的,包括请求方法,状态码,响应时间这些。 所以这个导出器虽然可以查看 nginx 的一些流量分布,但是并没有办法检测到有哪些 api 是慢返回的,甚至是异常状态码的。
prometheus-nginxlog-exporter
如果要解决上述的情况,我们应该是要抓取 nginx 的 access log 才对,因为上面的所有的信息都在 access log 上,因此我们只需要去解析 access log,并采集就行了。
后面找了一下,还真有专门解析 nginx-log 的 prometheus 的导出器: prometheus-nginxlog-exporter
这个导出器其实很强大,他可以导出多个站点的 nginx 的 access log 并采集,而且可以自定义一些标签
1. 安装
他有三种安装方式,我们可以依然采用二进制包的安装方式,具体安装如下:1
2
3
4# 下载并安装二进制包
[root@VM-16-223-centos ~]# cd /usr/local/
[root@VM-16-223-centos local]# wget https://github.com/martin-helmich/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter/releases/download/v1.9.2/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter_1.9.2_linux_amd64.rpm
[root@VM-16-223-centos local]# yum localinstall prometheus-nginxlog-exporter_1.9.2_linux_amd64.rpm
这样子就安装好了,然后查看一下运行状态:1
2
3
4
5[root@VM-16-223-centos etc]# sudo systemctl enable prometheus-nginxlog-exporter
[root@VM-16-223-centos etc]# systemctl status prometheus-nginxlog-exporter
● prometheus-nginxlog-exporter.service - NGINX metrics exporter for Prometheus
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
看样子是没有启动,查看一下 service 文件:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13[root@VM-16-223-centos etc]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter.service
[Unit]
Description=NGINX metrics exporter for Prometheus
After=network-online.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter -config-file /etc/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter.hcl
Restart=always
ProtectSystem=full
CapabilityBoundingSet=
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
然后看了一下,他默认的这个配置文件:1
/etc/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter.hcl
发现里面的配置不对,默认的 nginx access log 地址不对,需要要自己改, 而且我不太喜欢用 hcl,所以后面就改成 yml 的格式来处理,假设先获取某一个站点的 access log,所以就是:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11[kbz@VM-16-9-centos ~]$ cat /etc/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter.yml
listen:
port: 4040
metrics_endpoint: "/metrics"
namespaces:
- name: air_id
format: "$host $remote_addr \"$clientRealIp\" - - [$time_local] \"$request\" \"$status\" $body_bytes_sent \"$http_referer\" \"$http_user_agent\" $request_time $bytes_sent $request_length [$upstream_response_time]"
source:
files:
- /var/log/nginx/test.example.com.access.log
这边注意几个细节:
- namespaces 的 name 就是我们抛送指标的前缀,所以要符合指标的格式
- format 格式要按照你的 nginx 的 log_format 来搭建,如果发现没有数据,那么就是 format 有问题,这时候就可以看 error log 逐步排查
然后重新修改 service 文件将执行指令修改成:1
/usr/sbin/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter -config-file /etc/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter.yml
最后 restart 一下1
systemctl restart prometheus-nginxlog-exporter
就可以看到有开始抛送数据了:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11[kbz@VM-16-9-centos ~]$ curl http://localhost:4040/metrics
# HELP air_id_http_request_size_bytes Total amount of received bytes
# TYPE air_id_http_request_size_bytes counter
air_id_http_request_size_bytes{method="GET",status="200"} 4107
# HELP air_id_http_response_count_total Amount of processed HTTP requests
# TYPE air_id_http_response_count_total counter
air_id_http_response_count_total{method="GET",status="200"} 7
# HELP air_id_http_response_size_bytes Total amount of transferred bytes
# TYPE air_id_http_response_size_bytes counter
air_id_http_response_size_bytes{method="GET",status="200"} 55841
...
可以看到他的指标采集成功了,并且所有的指标都是以所配置的name air_id 作为前缀
同时如果要查看具体运行的 log,包括错误 log 的话,可以用:1
sudo journalctl -u prometheus-nginxlog-exporter -f
2. 添加到 prometheus 监控 instance
接下来将其添加到 file_sd/server-nginx.yml 的后面 (通过文件服务发现添加的新的实例不需要重启 prometheus)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9- targets:
- 172.19.16.9:4040
labels:
env: test
product_line: personal
region: jp
cloud_platform: tx
server_type: nginx-log
wan: 43.xx.xx.234
为了跟上面的 vts 导出器分开,这边是 server_type 改成 nginx-log。
接下来可以在 prometheus 后台查看指标了
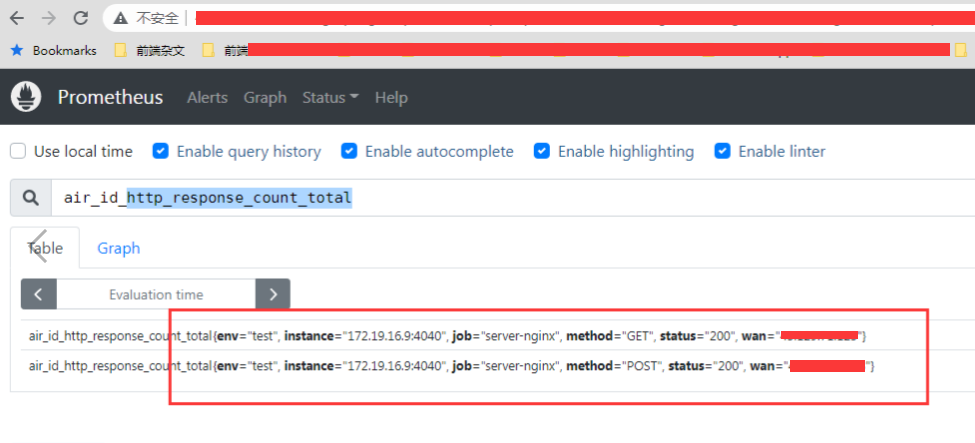
但是发现指标有采集正常了,但是标签里面还是没有 api,只有状态码和请求方法 ?? 最重要的 request_uri 标签竟然没有?
3. 添加 request_uri 标签
后面查了一下项目文档,其实是可以设置 request_uri 标签的,但是要改一下配置文件: custom_labels.feature
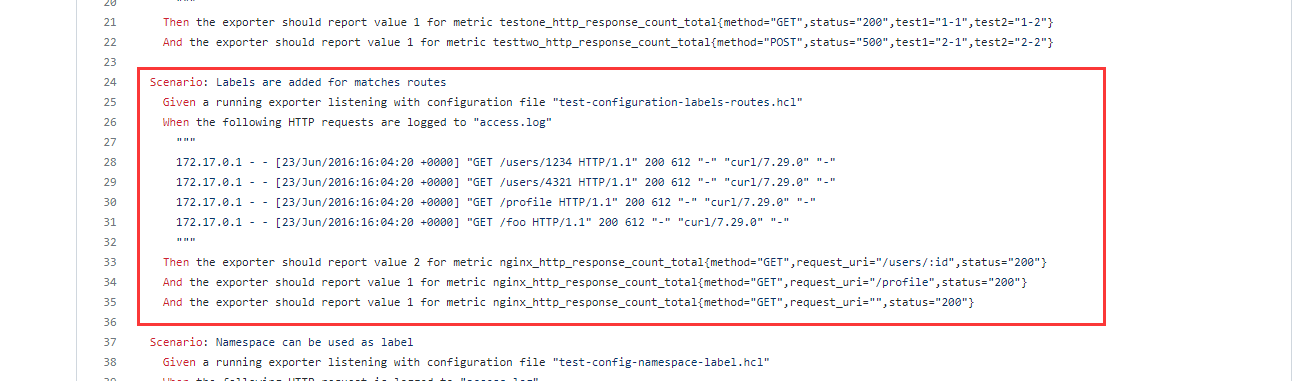
根据不同配置的 nginx 的 log 格式配置不一样,比如我这边 nginx log 的配置格式是:1
2
3log_format main '$host $remote_addr "$clientRealIp" - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'"$status" $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" '
'$request_time $bytes_sent $request_length [$upstream_response_time]';
那么设置的正则就是:1
format: "$host $remote_addr \"$clientRealIp\" - $remote_user [$time_local] \"$request\" \"$status\" $body_bytes_sent \"$http_referer\" \"$http_user_agent\" $request_time $bytes_sent $request_length [$upstream_response_time]"
后面参考了一下配置,最后形成的配置文件如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19[kbz@VM-16-9-centos ~]$ cat /etc/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter.yml
listen:
port: 4040
metrics_endpoint: "/metrics"
namespaces:
- name: air_id
format: "$host $remote_addr \"$clientRealIp\" - $remote_user [$time_local] \"$request\" \"$status\" $body_bytes_sent \"$http_referer\" \"$http_user_agent\" $request_time $bytes_sent $request_length [$upstream_response_time]"
source:
files:
- /var/log/nginx/test.example.com.access.log
relabel_configs:
- target_label: request_uri
from: request
split: 2
separator: ' '
matches:
- regexp: "^(.*?)(\\?.*)?$"
replacement: "$1"
其实就是加了 relabel_configs 配置, 大概的意思就是增加了 request_uri 标签,获取的途径就是获取 access log 中的 request 的值,然后通过空格拆分,获取第二个值,最后应用正则表达式获取 url path
这个正则表达式匹配的是一个字符串,该字符串可能包含一个问号,问号前的部分会被第一组捕获,问号及其后面的部分会被第二组捕获。如果没有问号,整个字符串会被第一组捕获。 简单来说就是匹配 url 字串中 ? 之前的部分。
所以原先的一条 access log 为:1
test.example.com xx.xx.xx.91 "xx.xx.xx.91" - - [13/Jan/2023:03:59:16 +0000] "GET /getcountrycode?csrf_token=xxxx&www_version=202301131143&callback=_jqjsp&_1673582348074= HTTP/2.0" "200" 65 "https://www.example.com/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/108.0.0.0 Safari/537.36" 0.032 346 1344 [0.032]
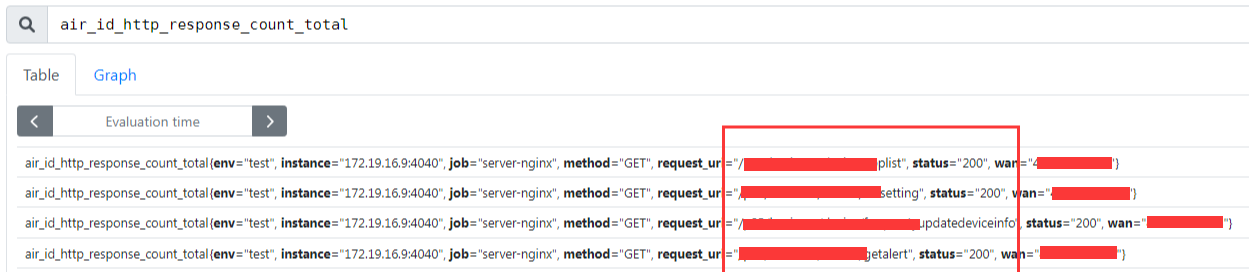
然后提取到的 request_uri 标签就是 /getcountrycode
因此就可以在 prometheus 后台看到这个 request_uri 的标签:
4. 再优化 – 兼容 grafana 的参数模板
试想一下,假设我们这一台服务器有部署了 3 个服务,每一个的 name 都不一样,分别是 id,srv,web。 然后同一个标签我们都要加上这个 name 前缀,才能查到具体的指标数据1
2
3id_http_response_count_total
srv_http_response_count_total
web_http_response_count_total
这样子看似没问题,但是如果我们放在 grafana 的 dashboard 上, grafana 的 dashboard 是支持参数的,我们要达到点击一下参数,就可以自动换成这个服务的对应的数据模板,比如这样子
如果要达到这个效果,那么当前的这种标签的指定方式是没办法实现的,因为每一个服务的相同含义的指标的名称不一样,没办法带入参数去配置。
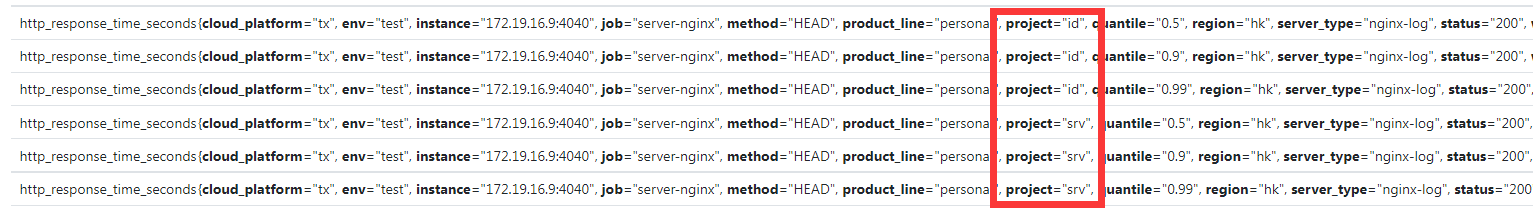
因此我们要将不同服务的指标的命名换一下,换成不同服务的指标名称相同,只不过多了一个 project 标签来表示不同服务,比如1
2
3id_http_response_count_total -> http_response_count_total{project="id"}
srv_http_response_count_total -> http_response_count_total{project="srv"}
web_http_response_count_total -> http_response_count_total{project="web"}
这样子我们只需要在 grafana 的 dashboard 创建一个 project 的参数,每次切换都可以换成不同服务的数据了。
后面查了一下官方文档,发现有一种写法是可以重写指标的前缀:1
2metrics_override:
prefix: "xx"
这样子就可以将指标的前缀重写为 xx,对于本例来说,就是为空
同时可以通过 namespace_label: "project" 增加一个 project 标签,而标签的值就是 namespace 的 name
所以最后的配置文件如下显示, 同时我们一下配置多个项目(增加一个 srv 项目的抓取):1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40[kbz@VM-16-9-centos ~]$ cat /etc/prometheus-nginxlog-exporter.yml
listen:
port: 4040
metrics_endpoint: "/metrics"
namespaces:
- name: id
format: "$host $remote_addr \"$clientRealIp\" - $remote_user [$time_local] \"$request\" \"$status\" $body_bytes_sent \"$http_referer\" \"$http_user_agent\" $request_time $bytes_sent $request_length [$upstream_response_time]"
source:
files:
- /var/log/nginx/test.example.com.access.log
# 设置前缀为空,后面好可以做参数配置
metrics_override:
prefix: ""
namespace_label: "project"
relabel_configs:
- target_label: request_uri
from: request
split: 2
separator: ' '
matches:
- regexp: "^(.*?)(\\?.*)?$"
replacement: "$1"
- name: srv
format: "$host $remote_addr \"$clientRealIp\" - $remote_user [$time_local] \"$request\" \"$status\" $body_bytes_sent \"$http_referer\" \"$http_user_agent\" $request_time $bytes_sent $request_length [$upstream_response_time]"
source:
files:
- /var/log/nginx/srv.example.com.access.log
metrics_override:
prefix: ""
namespace_label: "project"
relabel_configs:
- target_label: request_uri
from: request
split: 2
separator: ' '
matches:
- regexp: "^(.*?)(\\?.*)?$"
replacement: "$1"
这样子我们就可以看到同一个 nginx-log 实例的不同的项目的区别
5. grafana 设置 dashboard
接下来就是 grafana 后台设置 dashboard, 因为这个自定义的操作很多,因此在 dashboard 模板上,没有找到比较合适, 所以只能自己搭
同时因为我们标签筛选的层层级别很多,尤其是有些服务会涉及到多个区部署,因此我们设置的 dashboard 模板参数足足有 5 层
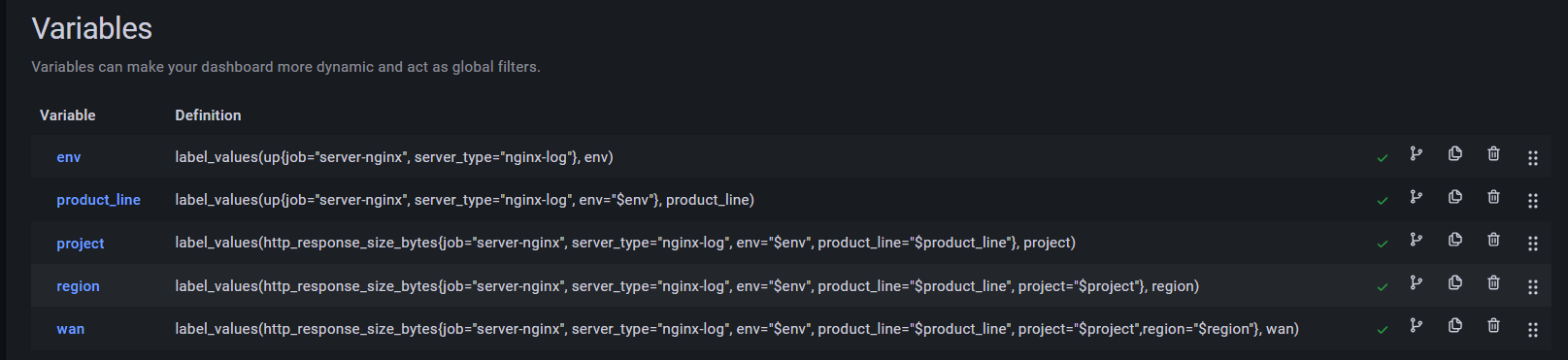
这边注意一个细节,到 project 层面上,就不能再用 up 指标了,因为具体收集的项目中,不会有 up 指标,而是要用具体有收集的指标,比如 http_response_size_bytes 等
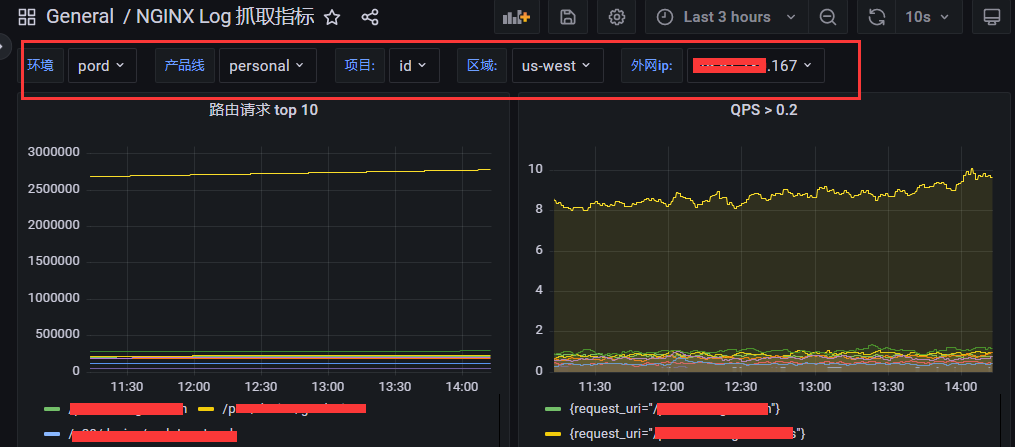
所以最后的 dashboard 效果就是:
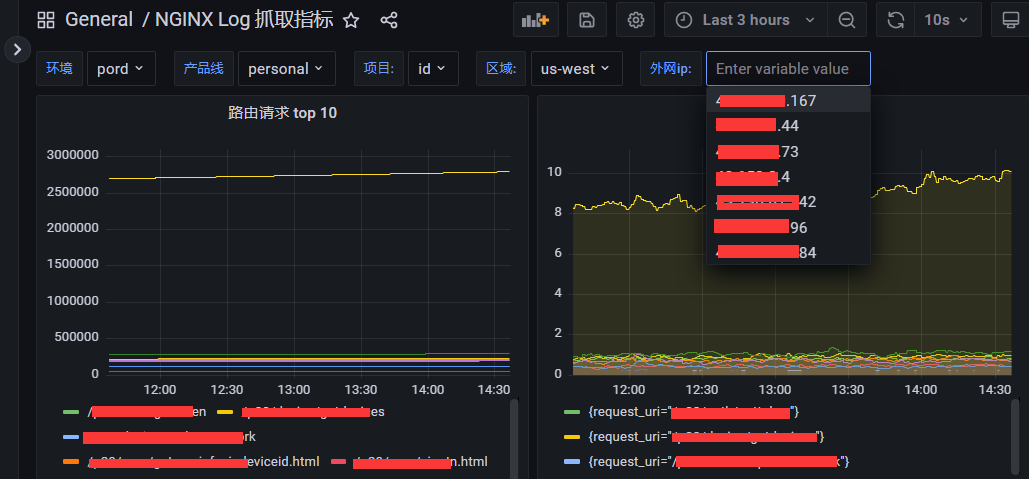
这样子只要将所有服务的 nginx log 都采集,无论我想看哪个环境,哪条产品线,哪个服务的哪个区域部署的哪台服务器的情况,都可以直接切换, 非常的方便
关于图表也是一样,要接参数,比如有一个图表叫 路由请求 top 10, 那么他的语句就是:1
sum(topk(10, http_response_count_total{job="server-nginx", server_type="nginx-log", env="$env",product_line="$product_line", region="$region", wan="$wan", project="$project", request_uri != ""})) by (request_uri)
比如我想知道有哪些请求的响应时间超过了 5s,那么就是:1
sum(http_response_time_seconds{job="server-nginx", server_type="nginx-log", env="$env",product_line="$product_line", region="$region", wan="$wan", project="$project", method!="OPTIONS" ,request_uri!="",status=~"2[0-9]*"} > 5) by (request_uri)
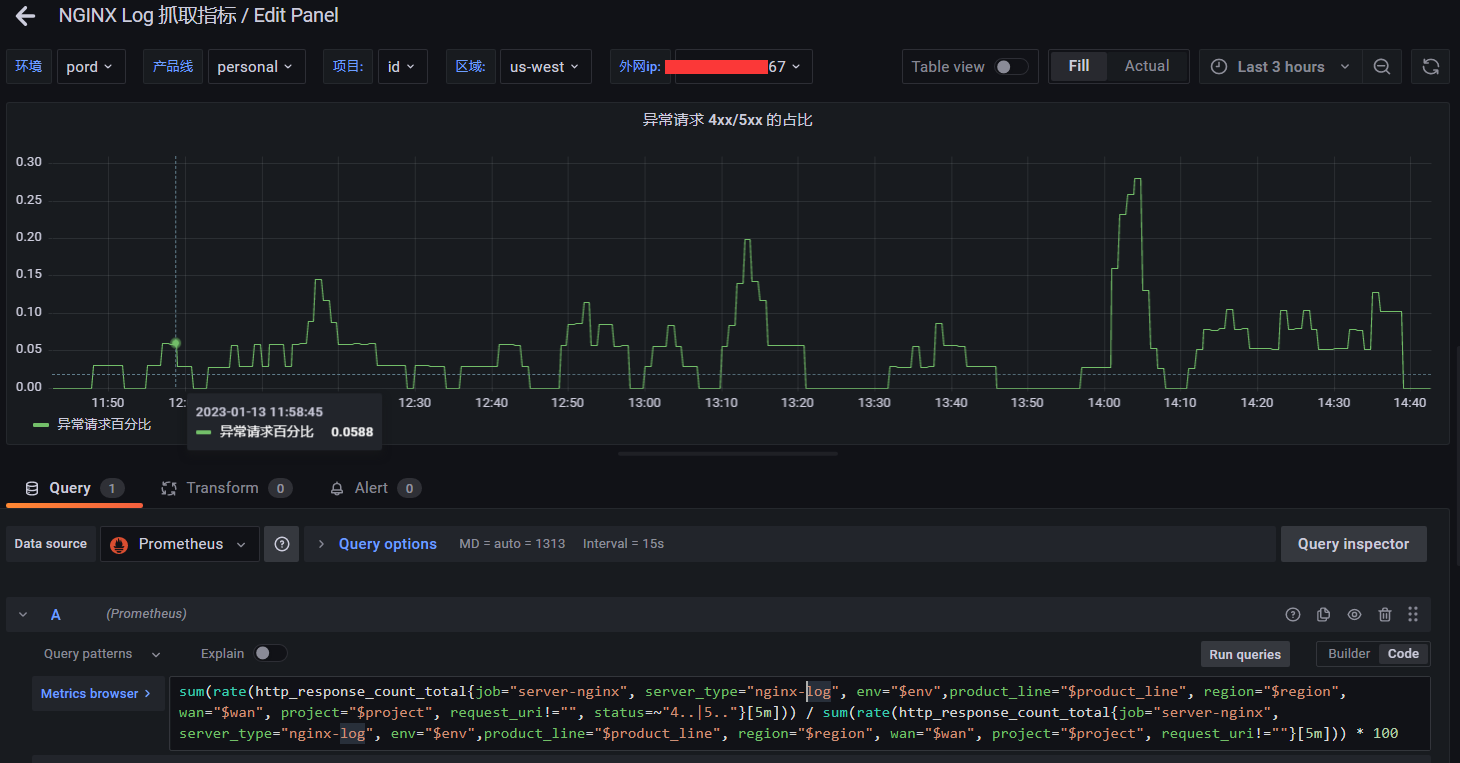
比如我想知道 4xx5xx 的占比,那么就是:1
sum(rate(http_response_count_total{job="server-nginx", server_type="nginx-log", env="$env",product_line="$product_line", region="$region", wan="$wan", project="$project", request_uri!="", status=~"4..|5.."}[5m])) / sum(rate(http_response_count_total{job="server-nginx", server_type="nginx-log", env="$env",product_line="$product_line", region="$region", wan="$wan", project="$project", request_uri!=""}[5m])) * 100
图表可以根据你具体业务的情况去调整参数值
后面在长期实践中,如果有确实很好用的图表和 PromQL 的话,再整理出来
遇到了一个 grafana topk 的坑
我之前在处理诸如 路由请求 top10 的时候,有使用过类似的 topk PromQL 语法:1
sum(topk(10, http_response_count_total{job="server-nginx", server_type="nginx-log", env="$env",product_line="$product_line", region="$region", wan="$wan", project="$project", request_uri != ""})) by (request_uri)
这个在 grafana 上是正常的。
但是我用 rate 再配合 topk 语法的话,就会有问题,不会限制最多 10 个,而是全部显示出来,也就是 topk 语法不生效
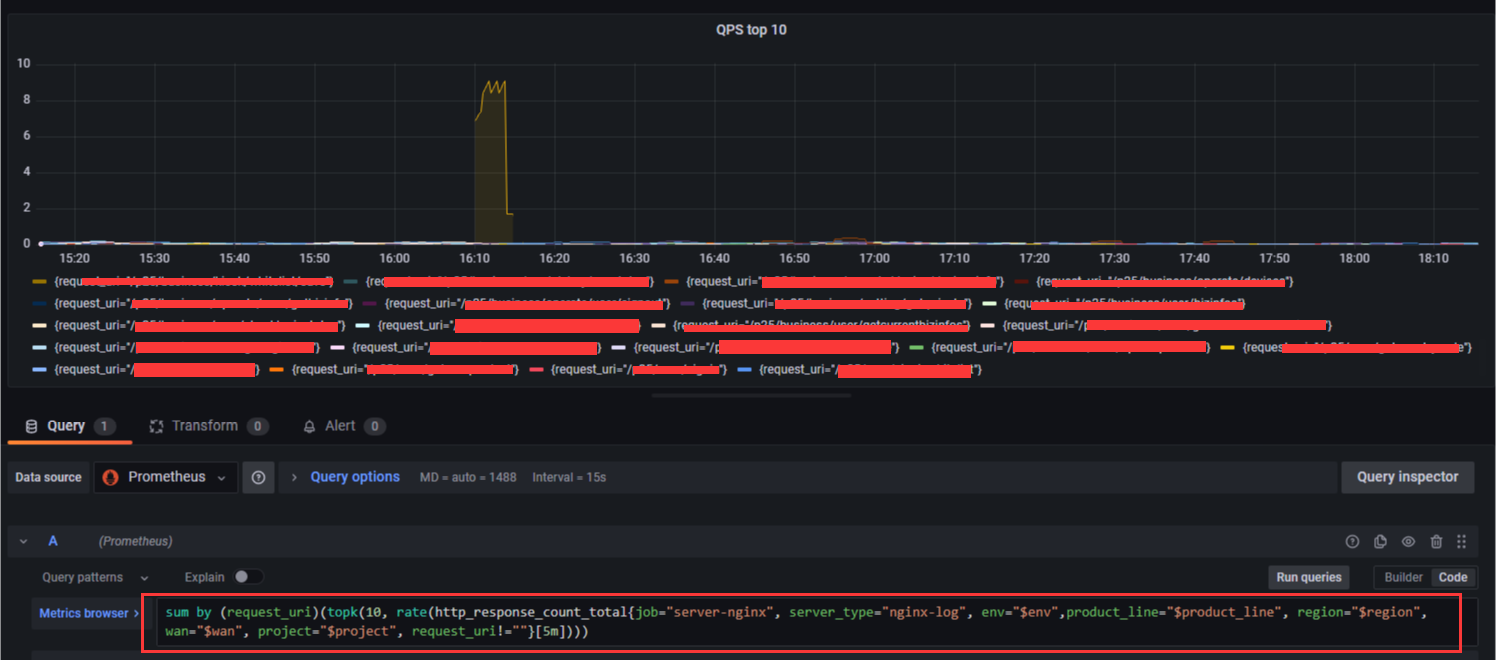
但是相同的语句在 prometheus 后台是可以的
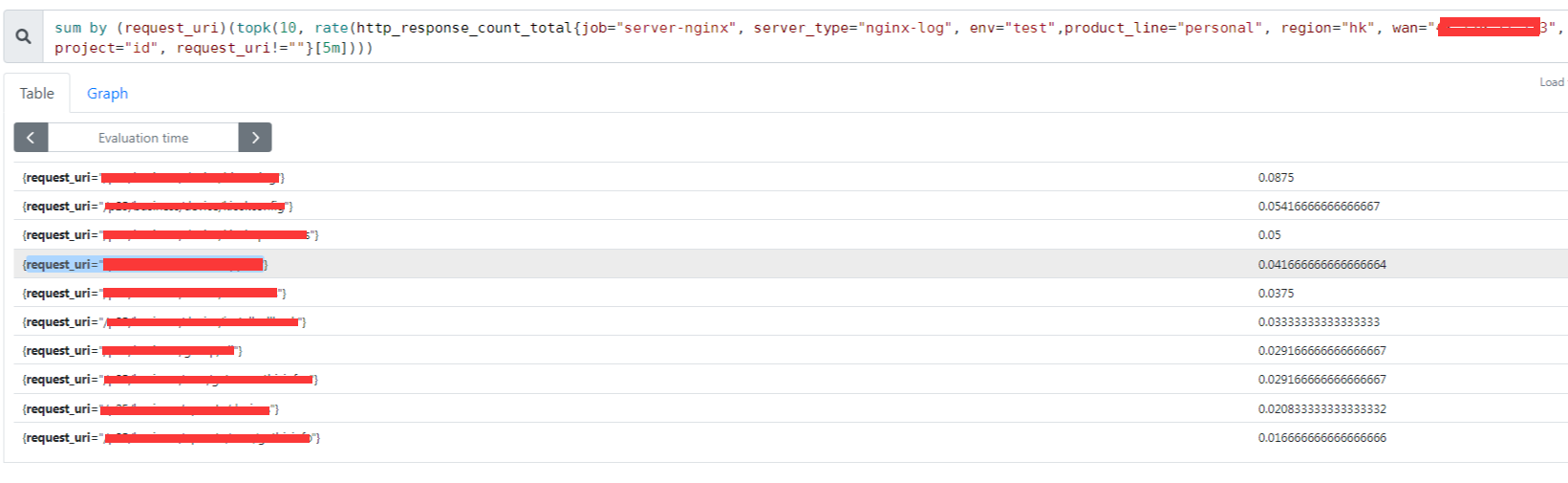
后面查了一下,其他人也有遇到这个问题:
- Prometheus topk returns more results than expected
- Prometheus topk and sort_desc provides additional metrics
后面发现需要开启图表的这个 instant 选项,也就是及时查询,这个就会正确的返回当前这个时间的 top10 了,但是因为是及时查询,所以只会有一个点
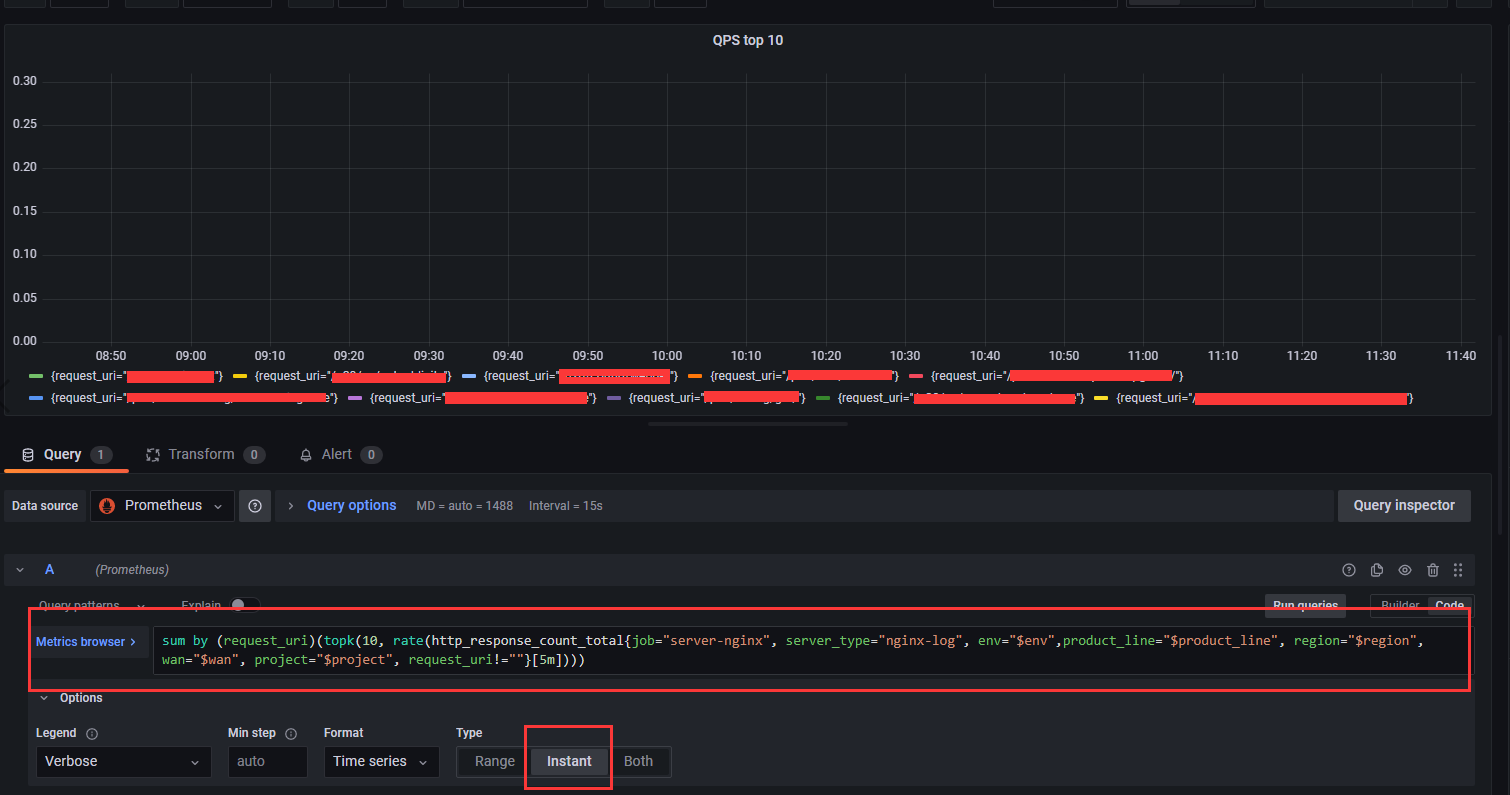
但是只有一个点,也满足不了我们的需求,所以就取一个临界值,比如要超过多少,才会显示:
1 | sum by (request_uri)(rate(http_response_count_total{job="server-nginx", server_type="nginx-log", env="$env",product_line="$product_line", region="$region", wan="$wan", project="$project", request_uri!=""}[5m]) > 0.2) |
6. 跟真实的 nginx-access.log 的延迟差距
事实上,Prometheus 采集到的数据,跟真实的 nginx-access.log 的记录是有存在一个采集周期的延迟。
因为 nginx-access.log 是实时录入的,而 Prometheus 是在当前周期采集上一个周期的数据的,假设你的采集周期是 60s。
那么你 Prometheus 在 07 分钟采集的数据,其实是对应 nginx-access.log 中的 06:00 -- 06:59 这个时间段的数据,所以在对数据的时候,其实是差一个采集周期的。
而且实际的生产环境中,考虑到 Prometheus 采集请求的网络延迟,一般是超过了一个采集周期再加几秒,比如如果是 60s 一个采集周期,那么Prometheus 在 07 分钟采集的数据, 这数据大部分就是在 nginx-access.log 中的 06:00 -- 07:05 这个时间段的数据
7. 跟进异常状态码并设置预警
我们之所以抓取 nginx 的 log,除了能够知道各个路由的 QPM 之外,还有就是为了在 nginx 出现异常状态码的时候,比如 499, 500, 502, 504 的时候,我们能够及时预警并第一时间跟进
因此就可以根据具体的业务,创建异常状态码的图表,以实际的 pay 支付服务为例,就要监控以上 4 种异常状态码的情况,当达到一定频率和数量的时候,能够及时预警
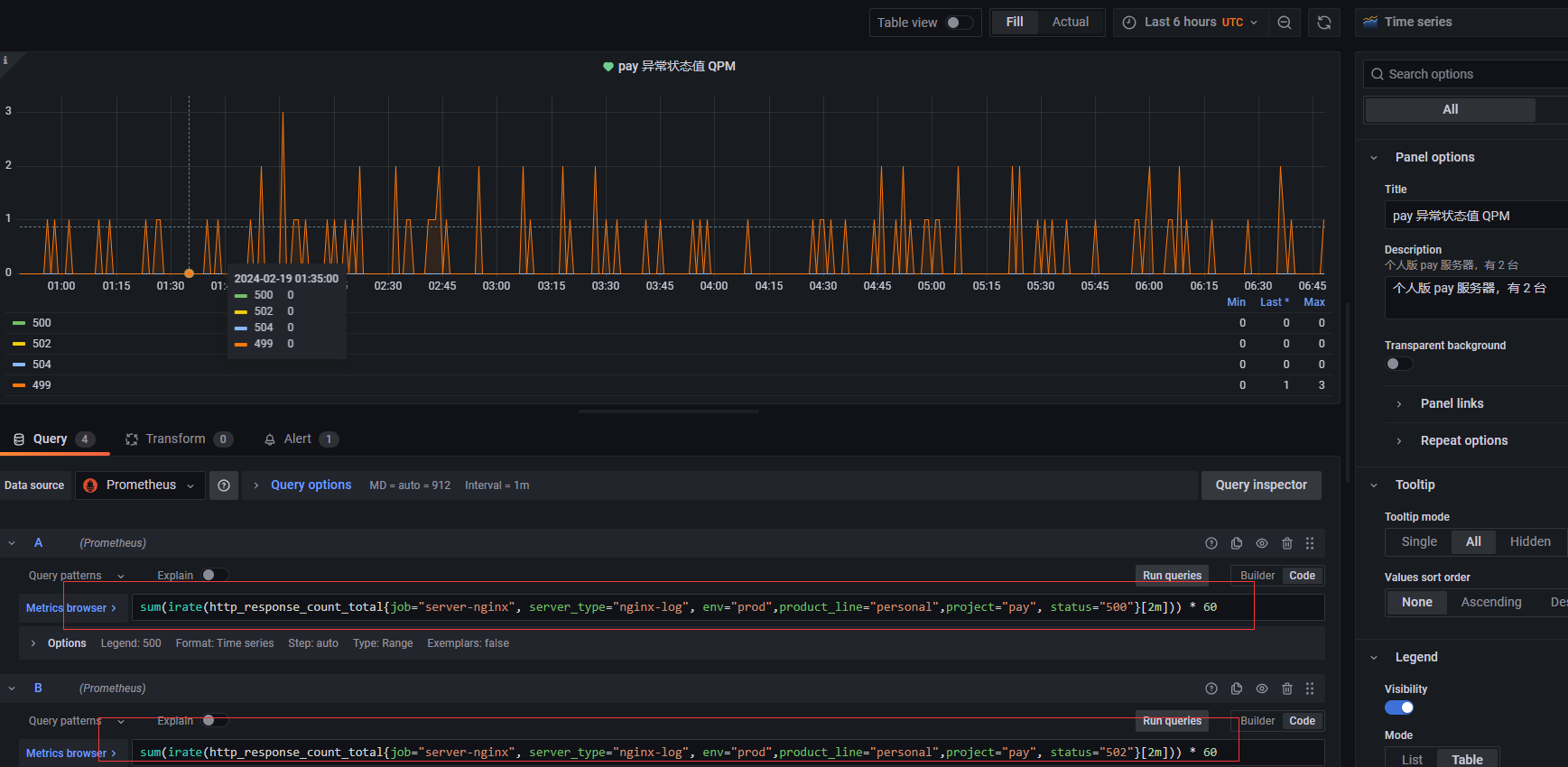
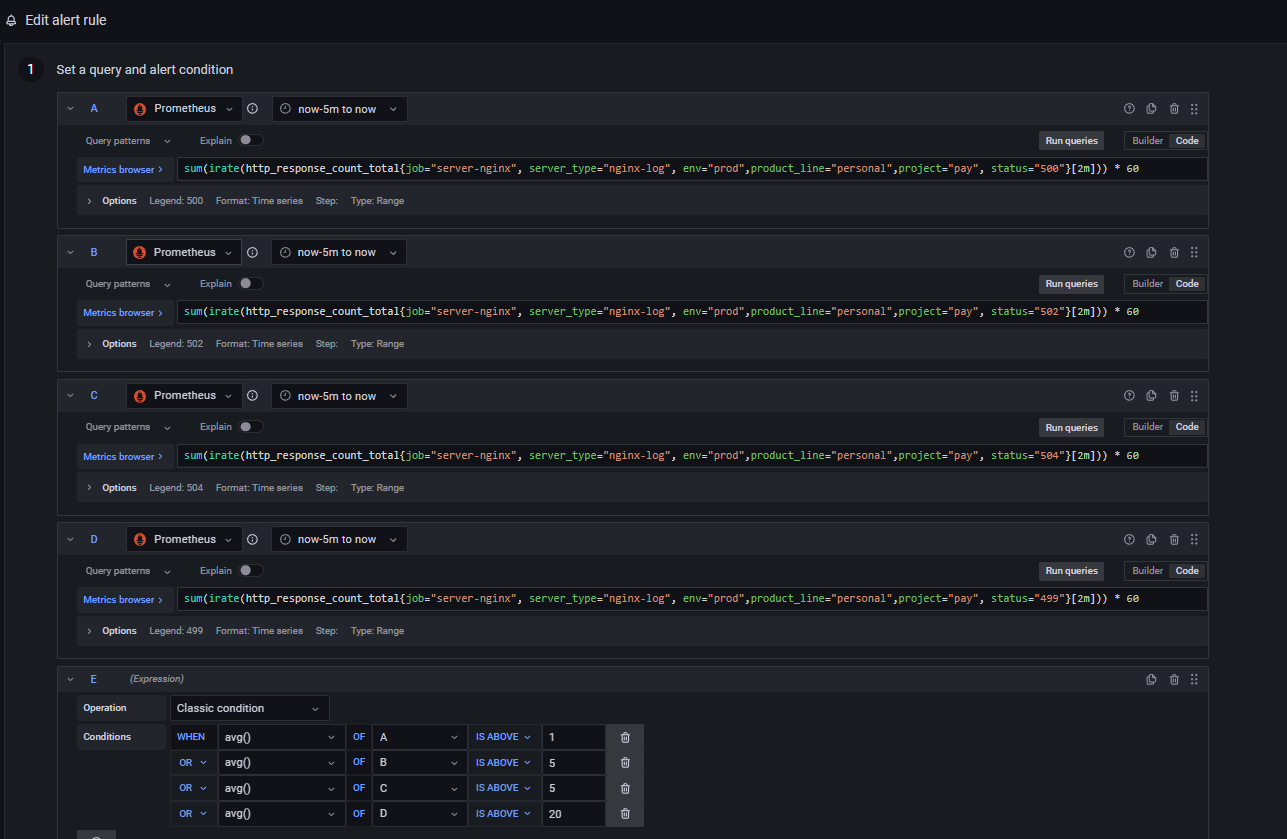
然后设置预警的时候,可以根据具体项目情况来设置,比如 499 状态码会有一定的数量容错,但是对于 500 这种状态码,基本上代表程序问题,应该马上跟进
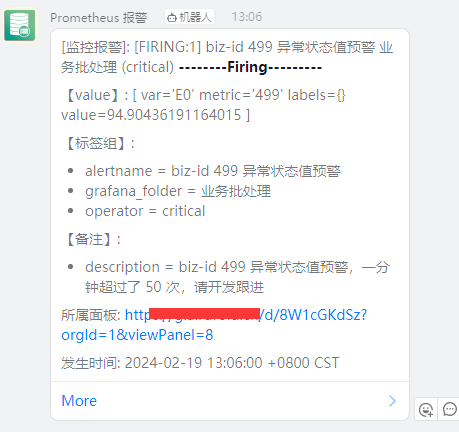
然后预警触发的时候,可以设置通知手段,比如邮件或者 钉钉通知之类的,比如这个就是我们触发 499 后,发送的钉钉通知
8. 内存消耗过多的情况
在实践过程中,有发现当出现 nginx 的 access log 特别大的时候,会出现这个 exporter 占用内存过多的情况。
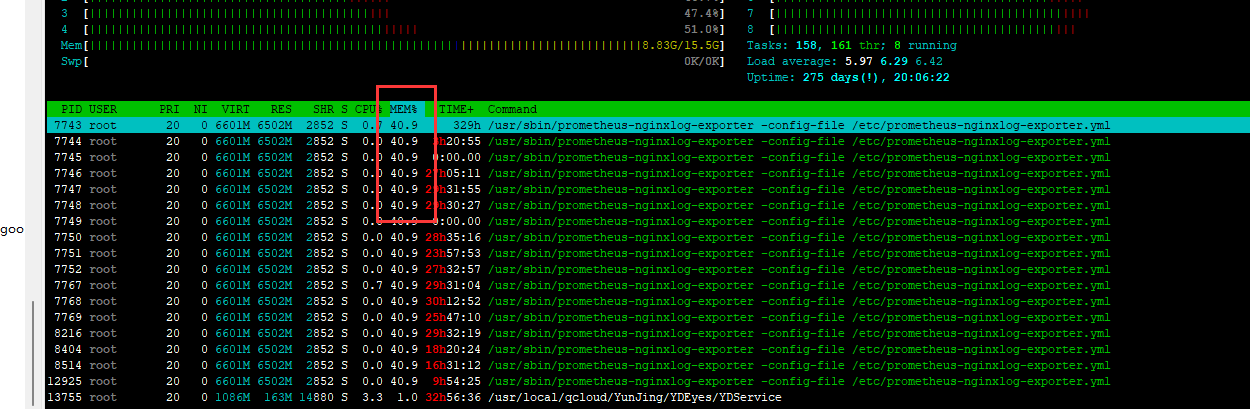
正常 nginx 的 access log 的日志归档是一天一次归档,但是发现在一些请求量特别大的项目,一天的 nginx 的 access log 就可以达到超过 6G 以上。
这时候这个 exporter 在统计的时候,因为需要将整个 access log 读取到内存中,然后进行统计,就会出现以下两个问题:
- exporter 占用的内存过大,甚至比业务程序所占用的内存大很多,这个是因为 access log 太大,导致统计读取到内存的时候,过多的占用服务器内存,从而可能会影响到业务
- 抓取统计的速度会越来越慢,甚至高峰期 Prometheus 来抓取的时候会超时,这也是因为要计算的数据太多了。
所以如果你的程序也有类似的情况的话,那 nginx 的 access log 就要按小时来归档,同时每一次脚本在归档的时候,也要重启这个 exporter,让它释放之前的内存,从而读取归档后的文件。
不过这样子也会有一个小小的问题,就是因为 exporter 每小时重启一次,释放内存,这时候因为有些数据是 counter 类型的,就会出现数据断掉,就会出现在整点那个时间抓取的数据,跟前面的数据关联不上
比如 QPM 和 QPS 这种 irate 计算方式,在整点 01 分的那个统计节点就会不准确。其他时间就会正常。
总结
通过 nginx-vts-export 和 prometheus-nginxlog-exporter 这两个导出器,我们基本上可以抓取 nginx 上的服务的情况,包括流量,请求等等。
当然掌握数据只是第一步,接下来就是要在实践中,慢慢摸索出适合你们项目的图表以及对应的预警处理。
参考资料: